MétéoCarbone® methodology
This technology, developed in partnership with the Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement, allows continuous monitoring of a territory’s CO2 emissions.
IG3IS -certified technology from World Meteorological Organisation (WMO)
IG3IS (Integrated Global Gas Information System) certification aims to identify and support greenhouse gas (GHG) monitoring technologies and projects that use inverse modelling.
Our solution has been recognised for its ability to provide accurate and reliable measurements of urban greenhouse gas emissions, enabling cities to effectively plan and monitor their emission reduction policies.
This makes MétéoCarbone® the first atmospheric GHG monitoring solution to be certified and ready for use at an urban, regional or national scale.
Find out how it work
Automated carbon inventory
Use activity data to estimate emissions in a given area.
MétéoCarbone® technology is designed to optimise the emissions data calculated for an area using an atmospheric measurement network and inverse modelling.
We start by automating the calculation of a territory’s greenhouse gas emissions. Our Automated Carbon Inventory provides an accurate estimate of the emissions generated by the various activities that occupy the area (industry, transport, waste, housing, etc.) on a hourly basis.
Reverse modelling
Compare the estimates from our model with the measurements from our sensors
Our atmospheric model accurately simulates the transport of CO2 in the atmosphere, taking into account the contributions of human activities, vegetation respiration and large-scale CO2 transport. We compare the CO2 emissions estimated by our inventory with the CO2 concentrations measured by our network of sensors scattered across the territory.
Reverse modelling and Bayesian optimisation allow us to adjust actual emissions based on concentration measurements from our sensors, providing accurate estimates of CO2 emissions.
We currently use the WRF-Chem model (Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry), developed collectively by the scientific community under the direction of NOAA. This model is a benchmark for weather forecasting and scientific research.
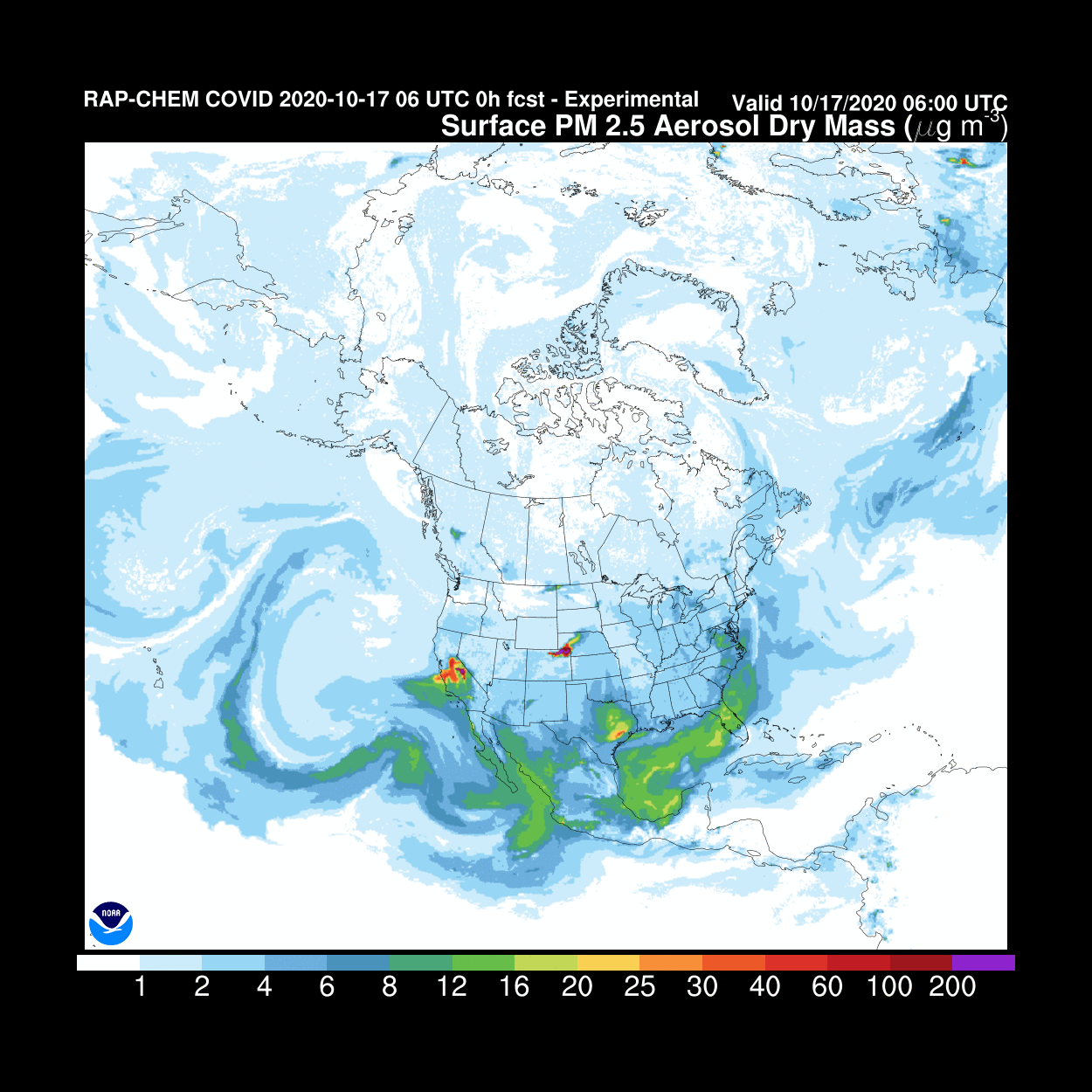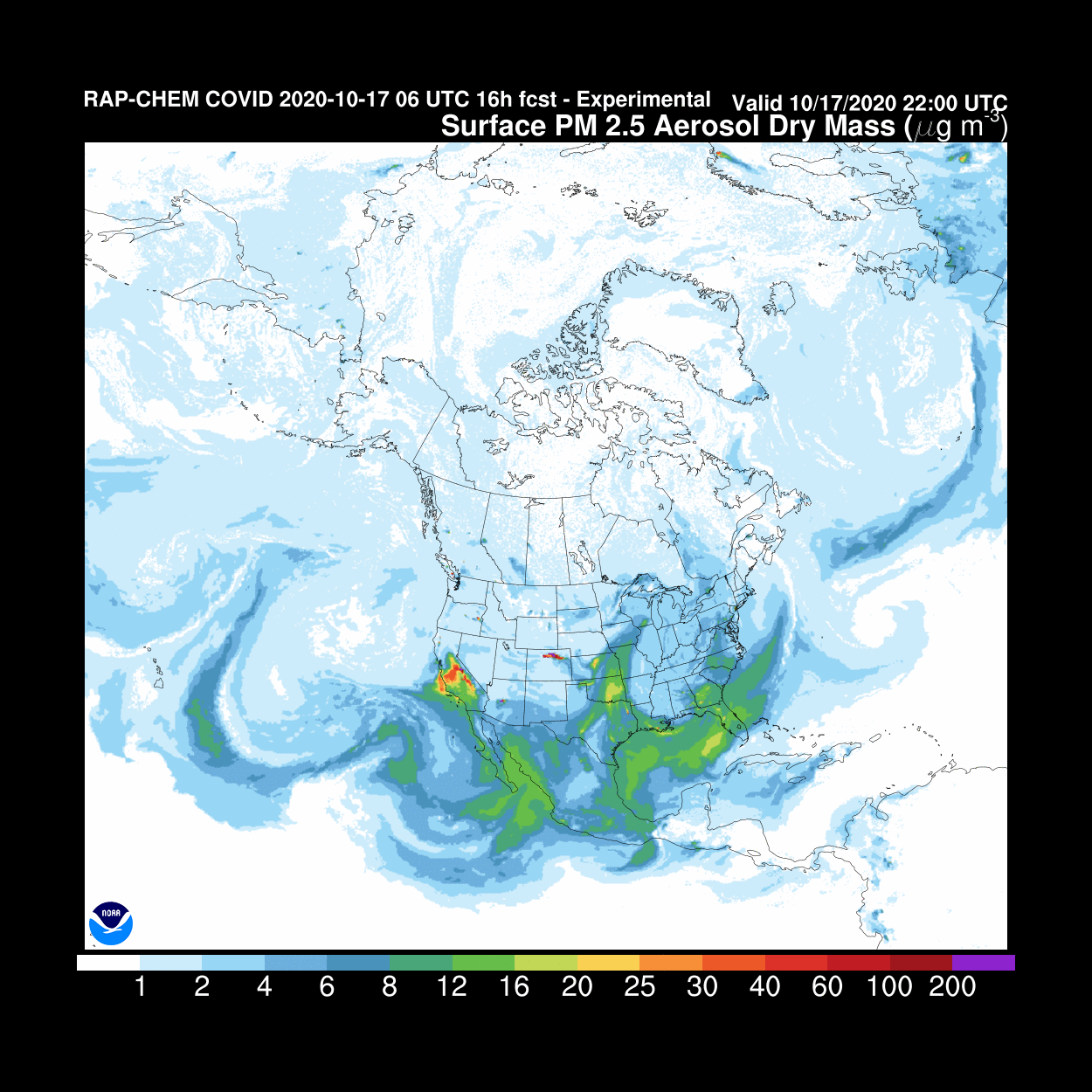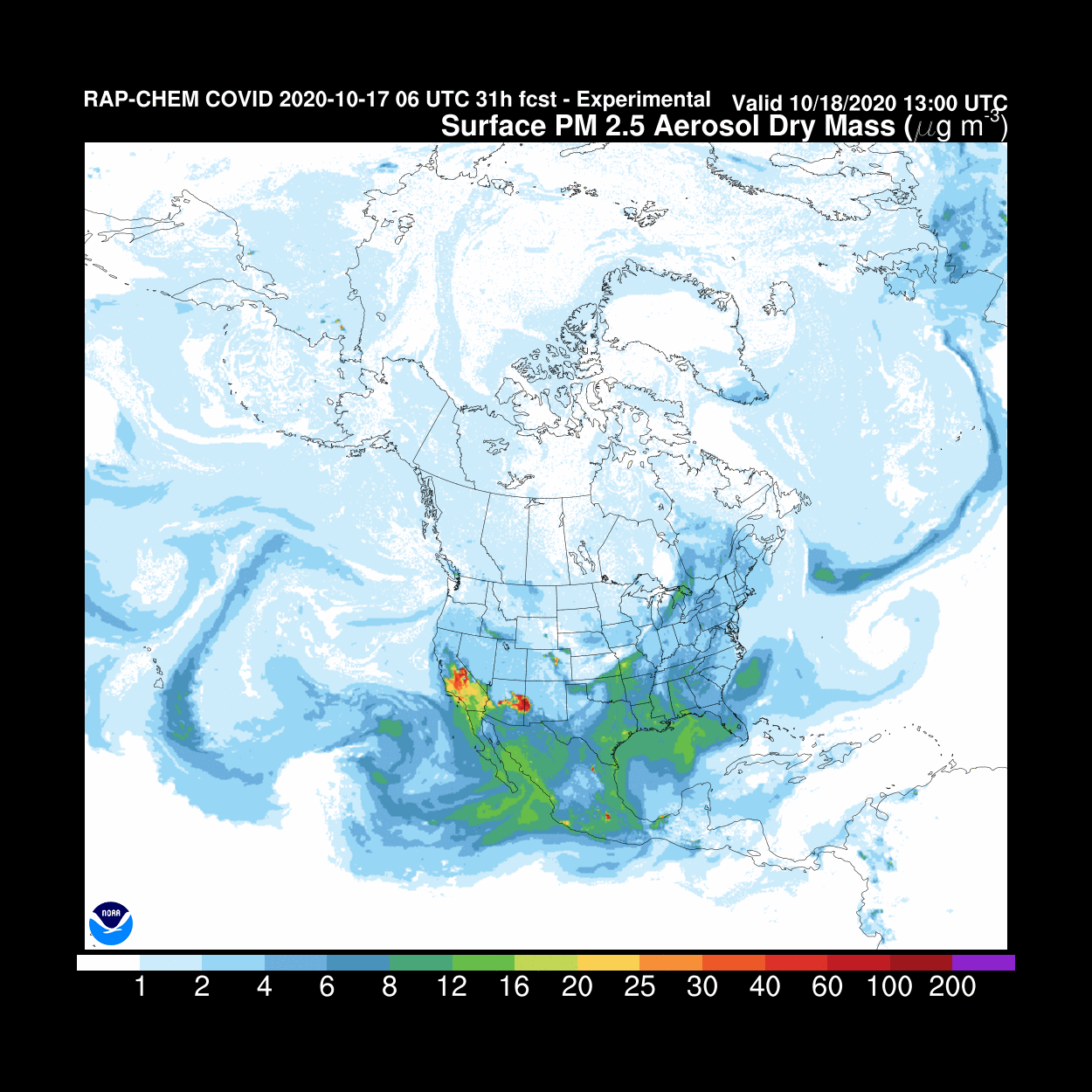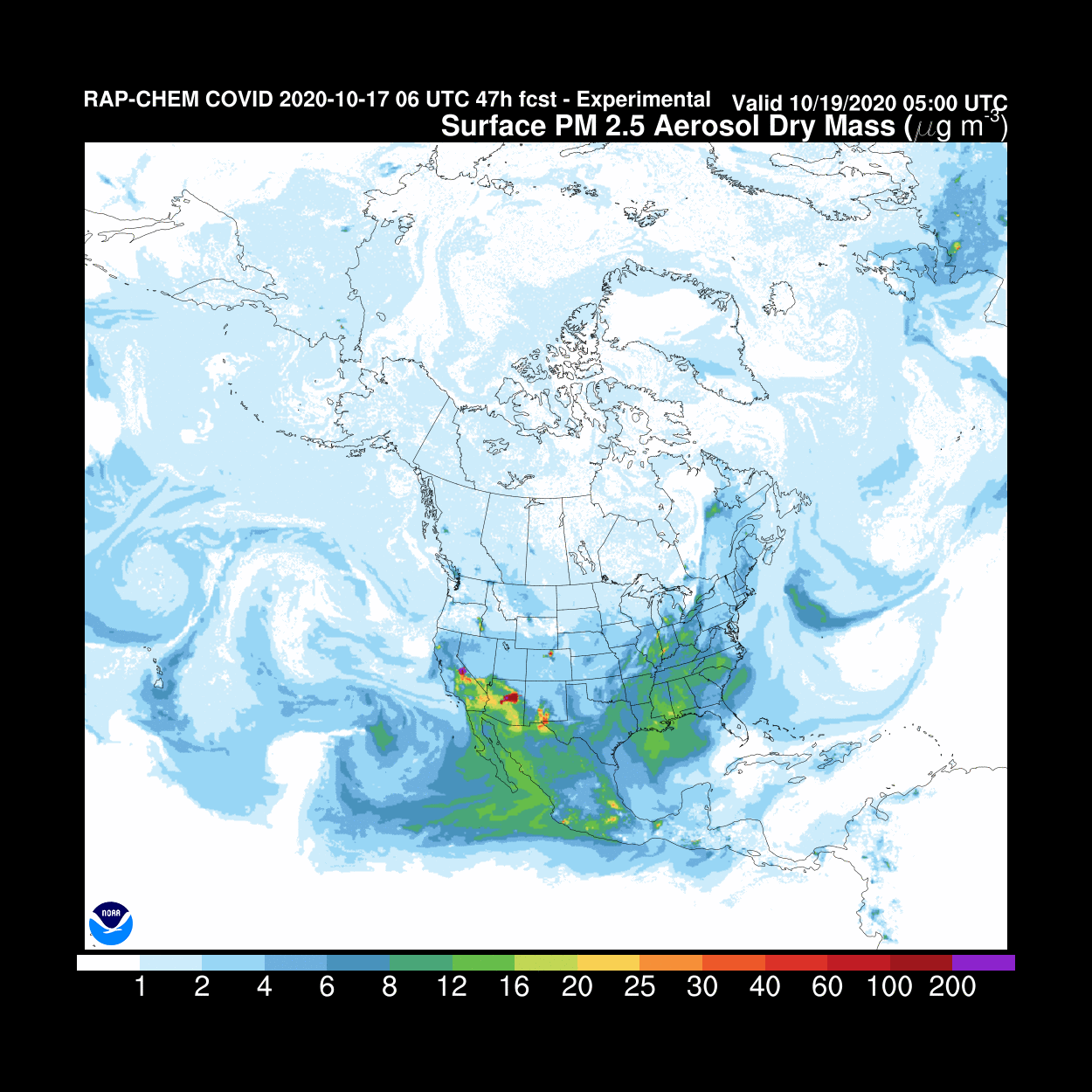
Source: NOAA
Atmospheric measurement
Continuous measurement to refine the calculation of local emissions
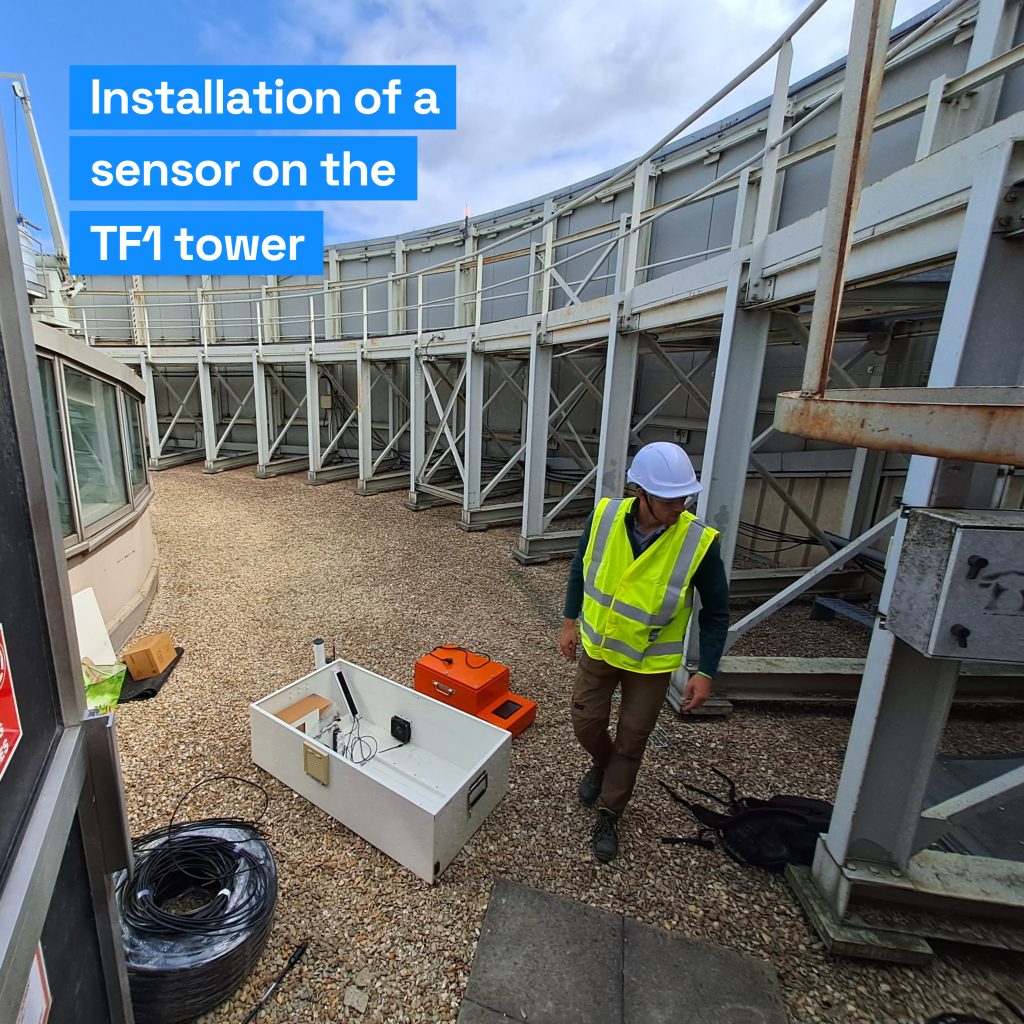
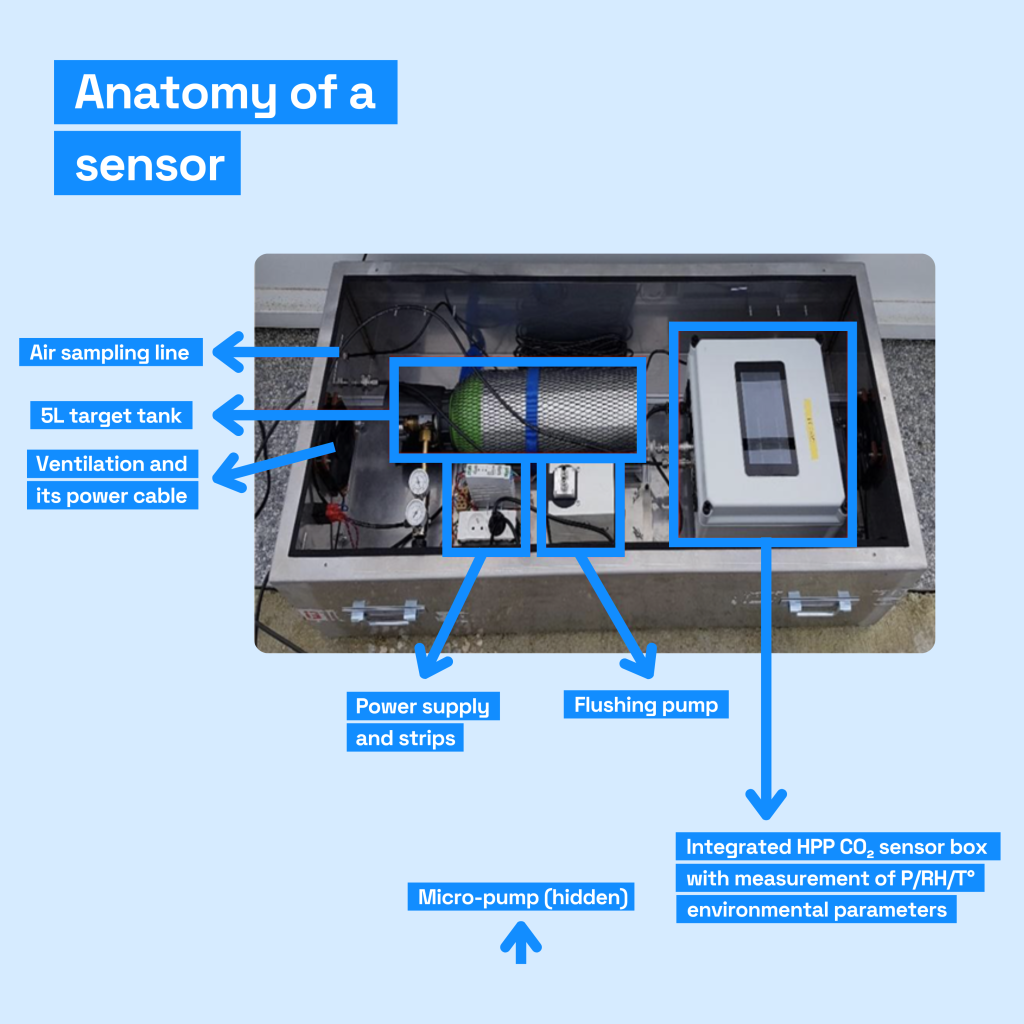
Our sensors accurately measure the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere before and after the wind. We position our sensors on roofs and strategically distribute them across the territory to ensure an accurate measurement of the background air.
Our sensors are the result of 10 years of joint research and development with the LSCE to develop sensors that combine cost and accuracy (1ppm).
By comparing observations from our measurement stations with model predictions, we will adjust the carbon inventory to improve its accuracy and compensate for the delay in publishing activity data.
Our inventory is calibrated by measurement, which allows us to provide day-to-day emissions data that is corrected for potential biases and errors in the source data.




Any questions?
Check out our FAQs for quick and accurate answers about our services, technology and much more.